
The last value is checked by using (last-first) %step = 0. The idea is to create a range of array indices and. The minimum value of progression is not less than the end value for negative step. In Kotlin, you can easily create ranges of values using the rangeTo() function and its operator form. The last element of the Progression is largest value not greater than the end value for positive step. The output generated by downTo() and step() functions is always a Progression. For example, a range type LongRange implements ClosedRange and extends Long Progression, it means all the operation which are defined for LongProgression is also available for LongRange. operator creates an object for integral type which implements both ClosedRange and Progression. As progression is Iterable type it can be used in for-loop and function such as filter, map etc. Progression refers to subtype of Iterable, where N is Char, Int or Long. The first element is first, sub-sequent elements represent previous element plus step and the last element is the last element unless progression is completed. Progressions represent the first element, the last element and the step which is non-zero.
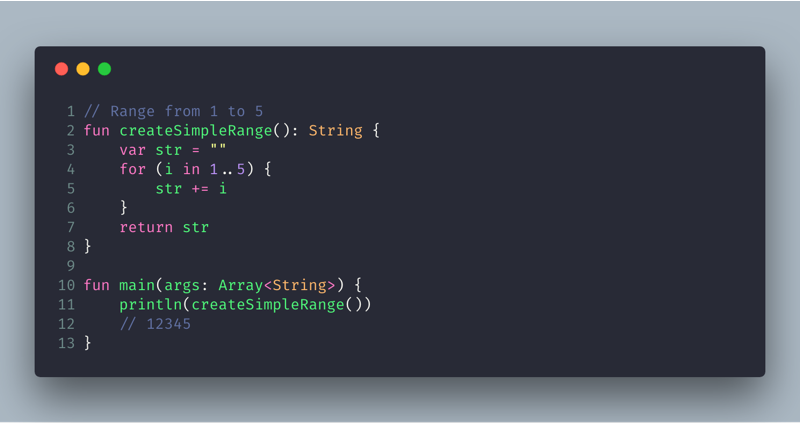
This is done by using in or !in operators.Īn arithmetic progression is represented by integral type progressions such as CharProgression, IntProgression, Long Progression. Kotlin range creation The following example shows how to create simple ranges in Kotlin. The distance between two values is defined by the step the default step is 1.

Kotlin ranges are inclusive by default that is, 1.3 creates a range of 1, 2, 3 values. The operation performed in range is to check whether the element is contained in it or not. operator or with the rangeTo and downTo functions. It contains two endpoints as start and end (endInclusive)points.

It represents a closed mathematical interval defined for comparable types. Ranges implement ClosedRange a common interface in the library. In Kotlin, for loop is used to iterate through the following because all of them provides iterator.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
